Currently Empty: RM0.00
Did you know that 70% of the immune system resides in the gut? This surprising fact highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy gut for overall well-being. Many people are confused about the roles of probiotics and prebiotics, but understanding their differences can unlock a path to better health.
Probiotics are live bacteria that support gut health, while prebiotics are the foods that feed these beneficial bacteria. Together, they create a synbiotic effect, enhancing digestion, boosting immunity, and improving mental well-being. Balancing gut flora is essential for a strong immune system and overall health.
Wellness Concept, a trusted name in health and wellness, is here to guide you. Reach out via WhatsApp at +60123822655 during business hours: Monday-Friday 9:30 am-6:30 pm, Saturday-Sunday 10 am-5 pm. This article will explain the roles of probiotics and prebiotics, their benefits, and how they contribute to a balanced diet.
Understanding these terms is key to making informed dietary choices. Whether through food or supplements, incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your routine can lead to a healthier, more balanced life. Let’s dive into the science in a friendly, easy-to-understand way.
Key Takeaways
- 70% of the immune system is located in the gut, making gut health crucial.
- Probiotics are live bacteria that support digestion and immunity.
- Prebiotics are foods that feed and enhance the effectiveness of probiotics.
- Combining probiotics and prebiotics creates a synbiotic effect for better health.
- Wellness Concept offers guidance via WhatsApp at +60123822655.
Understanding Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics play distinct yet complementary roles in gut health. While they sound similar, their functions are unique. Together, they help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which is essential for overall well-being.
Defining Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that support the gut by promoting a healthy balance of good bacteria. These beneficial organisms are found in fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut. They aid digestion, boost immunity, and even improve mental health.
Common strains include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Regular consumption of probiotic-rich foods can lead to better digestion and a stronger immune system.
Defining Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for probiotics. Found in foods like vegetables, whole grains, and artichokes, they help beneficial bacteria thrive. Prebiotics improve digestion, enhance calcium absorption, and regulate blood sugar levels.
Examples include inulin, found in chicory root, and resistant starch, present in unripe bananas. Including these in your diet ensures a healthy gut environment.
| Probiotic Foods | Prebiotic Foods |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Artichokes |
| Sauerkraut | Whole Grains |
| Kefir | Bananas (unripe) |
| Tempeh | Chicory Root |
Combining probiotics and prebiotics creates a powerful synergy for gut health. This approach ensures that beneficial bacteria are both introduced and nourished, leading to optimal digestion and overall wellness.
What’s the difference between probiotics and probiotics?
Probiotics come in various strains, each offering distinct benefits for the body. While they all support gut health, their mechanisms and effects can vary significantly. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right option for your needs.
Comparing Functions and Mechanisms
Different probiotic strains work in unique ways to support digestive and immune health. For example, Lactobacillus is known for aiding lactose digestion and reducing diarrhea. On the other hand, Bifidobacterium is effective in alleviating symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Another strain, Saccharomyces boulardii, a yeast probiotic, has shown promise in combating diarrhea and other digestive issues. These examples highlight how minor differences in strain and formulation can alter the overall benefit.
Highlighting Unique Benefits
Each probiotic strain offers specific advantages. Lactobacillus strains are commonly found in yogurt and fermented foods, making them accessible for daily consumption. Bifidobacterium, often present in dairy products, is particularly beneficial for those with IBS.
Here are some key benefits of popular strains:
- Lactobacillus: Improves lactose digestion and reduces diarrhea.
- Bifidobacterium: Alleviates IBS symptoms and supports gut health.
- Saccharomyces boulardii: Combats diarrhea and enhances digestive function.
The effect of these products may vary based on individual factors like body type and health conditions. For instance, some people may experience mild side effects like bloating during the initial days of consumption.
“The combination of probiotics and prebiotics creates a powerful synergy for gut health, ensuring beneficial bacteria are both introduced and nourished.”
Including prebiotic foods like whole grains and vegetables can enhance the efficacy of probiotic supplements. This approach ensures optimal digestion and overall wellness.
The Role of Gut Health and the Microbiome
The gut is often called the body’s second brain, and for good reason. It houses trillions of microorganisms that influence digestion, immunity, and even mental health. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for overall wellness, and understanding its role can help you make informed health choices.
Impact on Digestive System
The microbiome is a community of bacteria and other microorganisms that live in the digestive tract. These microbes break down food, produce essential vitamins, and create short-chain fatty acids that reduce inflammation. A healthy gut environment ensures efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
Probiotics and prebiotics play a key role in maintaining this balance. Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria, while prebiotics provide the fiber needed to nourish them. Together, they support a thriving gut ecosystem.
Supporting the Immune System
Did you know that 70% of the immune system resides in the gut? A healthy microbiome strengthens immune responses by producing anti-inflammatory compounds and regulating immune cells. This helps the body fight infections and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Research shows that certain strains of bacteria, like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, enhance immune function. Including probiotic-rich foods or supplements in your diet can boost your body’s natural defenses.
“A balanced gut microbiome is the foundation of a strong immune system and overall health.”
Here’s a quick look at how gut health impacts overall wellness:
- Digestion: Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients efficiently.
- Immunity: Produces compounds that fight infections and reduce inflammation.
- Mental Health: Communicates with the brain via the gut-brain axis.
| Key Functions of Gut Microbiome | How to Support It |
|---|---|
| Digestion and Nutrient Absorption | Consume probiotic and prebiotic foods. |
| Immune System Regulation | Include diverse, fiber-rich foods in your diet. |
| Production of Vitamins | Eat fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi. |
For those experiencing digestive issues, incorporating probiotics for digestive issues can be a game-changer. A healthy gut is the foundation of a strong immune system and overall wellness.
Dietary Sources: Fermented Foods and Prebiotic-Rich Options
Maintaining a healthy gut starts with the right foods. Incorporating a variety of fermented foods and prebiotic-rich options into your diet can significantly improve gut health. These choices work together to foster a balanced microbiome, supporting digestion, immunity, and overall wellness.
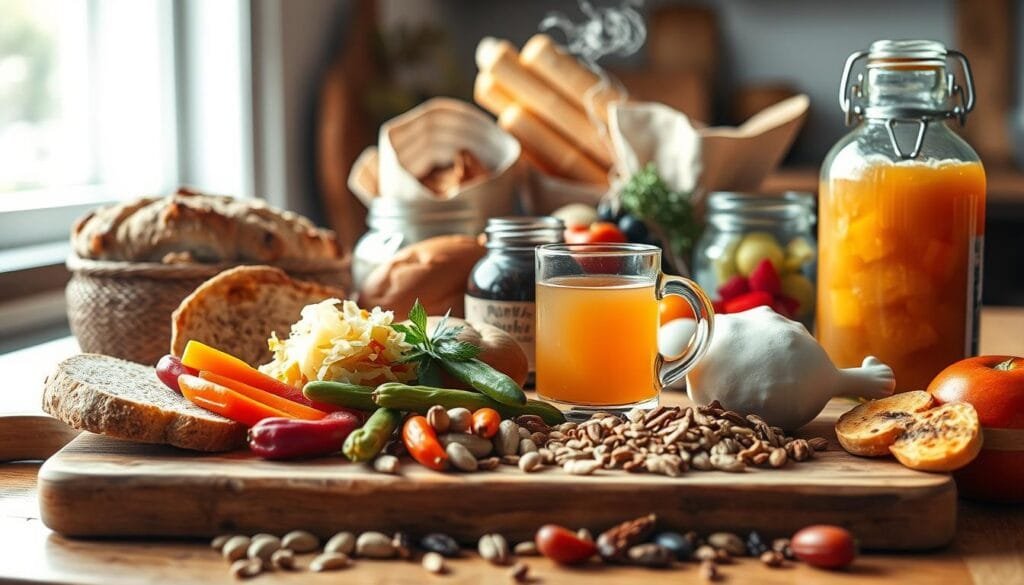

Top Probiotic Foods
Fermented foods are excellent sources of live beneficial bacteria. Yogurt, for example, contains lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria, which improve digestion and boost immunity. Other probiotic-rich options include kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi. These foods introduce live microorganisms that help maintain a healthy gut environment.
Here are some top probiotic foods to consider:
- Yogurt: Rich in lactic acid bacteria, supports digestion and bone health.
- Kefir: Contains diverse strains of friendly bacteria and yeast.
- Sauerkraut: High in fiber and antioxidants, promotes eye health.
- Kimchi: Packed with vitamins and iron, supports immune function.
Prebiotic Food Choices
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Foods like bananas, asparagus, and legumes are excellent sources. Whole grains, such as oats and barley, also provide prebiotic fiber. Including these in your diet ensures that probiotics thrive and function effectively.
Here are some prebiotic-rich options to add to your meals:
- Bananas: Unripe bananas contain resistant starch, a powerful prebiotic.
- Asparagus: High in inulin, supports gut bacteria growth.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils are rich in fiber, enhancing digestion.
- Whole Grains: Oats and barley provide sustained energy and gut health benefits.
| Probiotic Foods | Prebiotic Foods |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Bananas |
| Kefir | Asparagus |
| Sauerkraut | Legumes |
| Kimchi | Whole Grains |
Combining probiotic and prebiotic foods creates a powerful synergy for gut health. This approach ensures that beneficial bacteria are both introduced and nourished, leading to optimal digestion and overall wellness. Start by adding a variety of these foods to your diet for a healthier, more balanced life.
Probiotic and Prebiotic Supplements: Quality and Usage
Supplements can be a game-changer for gut health when chosen wisely. They offer a convenient way to introduce beneficial microorganisms and nourish the bacteria in your gut. However, not all products are created equal. Understanding how to select, store, and use them effectively ensures maximum benefits.
Choosing Effective Supplements
When selecting a probiotic supplement, look for verified quality and specific strain types. Products with Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium are commonly recommended for digestive health. Always check the label for the number of live microorganisms, as this indicates potency.
For a prebiotic probiotic supplement, ensure it contains both live bacteria and fibers like inulin or resistant starch. Combining these elements creates a synbiotic effect, enhancing overall gut health. Reputable brands often provide third-party testing results for added assurance.
Consulting a doctor is advisable, especially for individuals with specific health conditions. They can recommend the best product tailored to your needs.
Storage Tips and Safety Guidelines
Proper storage is crucial to maintain the efficacy of live microorganisms. Most probiotic supplements require refrigeration to preserve their potency. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure the bacteria remain active.
Safety is another key consideration. While side effects are rare, some individuals may experience mild bloating or discomfort initially. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help your body adjust.
Combining supplements with prebiotic-rich foods like whole grain or bananas can enhance their effectiveness. This approach ensures that the beneficial bacteria thrive and support your gut health.
“Quality and proper usage are the cornerstones of effective supplementation for gut health.”
| Supplement Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Probiotic Supplement | Contains live microorganisms like Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium. |
| Prebiotic Probiotic Supplement | Combines live bacteria with fibers like inulin for a synbiotic effect. |
| Storage Requirements | Often requires refrigeration to maintain potency. |
For more insights on the role of probiotics and prebiotics, explore our detailed guide on gut health supplements. Making informed choices ensures you get the most out of your wellness journey.
Integrating Prebiotics and Probiotics into Daily Life
Balancing your gut health doesn’t have to be complicated. With a few simple changes, you can incorporate prebiotics and probiotics into your daily routine. These adjustments can lead to significant improvements in digestion, immunity, and overall well-being.

Healthy Eating Guidelines for Gut Balance
Start by diversifying your diet with a mix of fermented and fiber-rich foods. Yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut are excellent sources of probiotics. Pair them with prebiotic foods like bananas, oats, and asparagus to nourish beneficial bacteria.
Here are some practical tips to get started:
- Plan your meals: Include at least one probiotic and one prebiotic food in each meal.
- Snack smart: Choose nuts, seeds, or whole grain crackers for a gut-friendly snack.
- Stay consistent: Regular consumption is key to maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
Variety is essential. Rotate different probiotic and prebiotic sources to ensure your gut remains diverse and healthy. For example, alternate between yogurt, kimchi, and tempeh for probiotics, and switch between oats, garlic, and legumes for prebiotics.
“Small, consistent changes in your diet can lead to long-term benefits for your gut and overall health.”
Combining these foods not only supports digestion but also strengthens your immune system. A healthy gut microbiome plays a crucial role in fighting infections and reducing inflammation.
For more detailed insights on the synergistic effects of prebiotics and probiotics, explore our comprehensive guide. Start today, and take the first step toward a healthier, more balanced life.
Conclusion
A balanced gut health is the foundation of overall well-being. Incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your daily routine can transform your digestive and immune systems. Prebiotics, found in foods like bananas and whole grains, nourish beneficial bacteria, while probiotics, present in yogurt and sauerkraut, introduce live microorganisms that support a thriving gut microbiome.
Combining these elements creates a powerful synergy, enhancing digestion and boosting immunity. For those seeking additional support, high-quality supplements can be a convenient option. Always consult a doctor to choose the right product for your needs.
Wellness Concept is here to guide you on your journey to better health. Reach out via WhatsApp at +60123822655 during business hours: Monday-Friday 9:30 am-6:30 pm, Saturday-Sunday 10 am-5 pm. Take the first step toward a healthier, more balanced life today!
FAQ
What are probiotics and how do they work?
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often called “good bacteria,” that support gut health. They help maintain a balanced microbiome, improve digestion, and boost the immune system by crowding out harmful bacteria.
What are prebiotics and why are they important?
Prebiotics are types of fiber that feed beneficial gut bacteria. Found in foods like garlic, onions, and whole grains, they promote the growth of probiotics, enhancing gut health and overall wellness.
Can I take prebiotics and probiotics together?
Yes, combining prebiotics and probiotics can be beneficial. Prebiotics act as food for probiotics, helping them thrive in the gut. This synergy supports a healthier digestive system and immune function.
What are some common sources of probiotics?
Probiotics are found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. These foods contain live cultures that contribute to a balanced gut microbiome.
Which foods are rich in prebiotics?
Prebiotic-rich foods include bananas, asparagus, Jerusalem artichokes, beans, and whole grains. These foods provide the fiber needed to nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
Are probiotic supplements effective?
Probiotic supplements can be effective, especially when they contain multiple strains and high CFU counts. It’s important to choose quality products and consult a doctor for personalized advice.
How can I improve my gut health naturally?
Eating a variety of fermented foods, prebiotic-rich vegetables, and whole grains can naturally improve gut health. Staying hydrated, managing stress, and avoiding processed foods also play a role.
Are there any side effects of taking probiotics?
Some people may experience mild side effects like bloating or gas when starting probiotics. These usually subside as the body adjusts. Consulting a healthcare provider can help minimize discomfort.
How do prebiotics and probiotics support the immune system?
Both prebiotics and probiotics help maintain a healthy gut, which is closely linked to immune function. They strengthen the gut barrier, reduce inflammation, and enhance the body’s ability to fight infections.
What should I look for in a probiotic supplement?
Look for supplements with multiple strains, high CFU counts, and clear storage instructions. Checking for third-party testing and expiration dates ensures quality and effectiveness.