Currently Empty: RM0.00
Did you know that nonalcoholic fatty liver affects up to 40% of adults in Western countries? This condition is becoming a global concern, and recent studies highlight the role of gut microbiota in its development. Research from platforms like Google Scholar reveals that certain supplements can improve intestinal barrier function and reduce inflammation, offering hope for those managing this condition.
In Malaysia, Wellness Concept is at the forefront of exploring these advancements. Their team provides expert insights and local initiatives to help individuals understand the connection between gut and liver functions. With a focus on fatty liver disease, they emphasize the importance of maintaining a balanced microbiome for overall well-being.
For more information, contact Wellness Concept via WhatsApp at +60123822655. Their business hours are Monday to Friday, 9:30 am to 6:30 pm, and Saturday to Sunday, 10 am to 5 pm. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into how specific interventions can support liver function in the sections ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver impacts up to 40% of adults globally.
- Gut microbiota plays a key role in liver conditions.
- Wellness Concept offers expert insights in Malaysia.
- Contact them at +60123822655 for more details.
- Business hours: Mon-Fri 9:30 am-6:30 pm, Sat-Sun 10 am-5 pm.
Overview of Probiotic on Liver Health
Emerging research highlights the role of gut bacteria in supporting liver wellness. Studies accessible via Google Scholar show that maintaining a balanced gut microbiome can significantly impact liver function. This is particularly relevant for conditions like fatty liver, which affects millions globally.
One key benefit is the improvement of gut barrier function. A healthy gut barrier prevents harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream, reducing inflammation and stress on the liver. This mechanism is crucial for managing liver disease and promoting overall well-being.
Recent reviews also emphasize the role of probiotics in regulating liver enzymes. For instance, a systematic review found that probiotic supplementation can lower enzyme levels, indicating better liver health. These findings are supported by clinical trials and meta-analyses.
In Malaysia, Wellness Concept is leading the way in exploring these advancements. Their local initiatives focus on educating the public about the gut-liver connection and promoting preventive measures. For more details, contact them at +60123822655.
This overview sets the stage for a deeper dive into specific liver conditions and the science behind probiotic interventions. Stay tuned as we explore these topics in the sections ahead.
Understanding NAFLD and Liver Disease
The rise of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a significant health issue, linked to modern lifestyle factors. This condition, characterized by fat accumulation in the liver, affects millions globally. It is the most common chronic liver disease, with its prevalence increasing due to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Defining Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD occurs when more than 5% of liver tissue is composed of fat. It ranges from simple steatosis (fat buildup) to more severe forms like steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. Insulin resistance and fat accumulation are primary indicators of the disease.
Identifying Risk Factors and Symptoms
Several factors increase the risk of developing NAFLD:
- Obesity: Excess weight is a major contributor.
- Type 2 diabetes: This condition doubles the risk of severe liver disease.
- Poor diet: High sugar and fat intake exacerbate the condition.
Symptoms are often silent in early stages but may include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and elevated liver enzymes.
Research from meta meta-analysis studies highlights the multifactorial nature of NAFLD. Probiotic supplementation has shown promise in reducing inflammation and improving liver function. For instance, clinical trials indicate that probiotics can lower liver enzyme levels and enhance gut barrier function.
Understanding NAFLD is crucial for early intervention. With lifestyle changes and targeted treatments, managing this condition becomes more achievable. Stay informed and proactive to safeguard your well-being.
The Gut-Liver Axis Explained
The gut-liver axis is a fascinating biological connection that plays a vital role in overall wellness. This pathway links the digestive system to the liver, allowing them to communicate and maintain balance. Research shows that disruptions in this axis can lead to chronic conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
One key aspect of this connection is gut permeability. When the intestinal barrier weakens, harmful substances like endotoxins can enter the bloodstream. This triggers inflammation and stress on the liver, worsening conditions such as insulin resistance. Clinical trials have shown that improving gut health can reduce these risks.
Recent studies highlight the role of tight junction proteins in maintaining gut integrity. These proteins act as gatekeepers, preventing harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream. Probiotic interventions have been shown to strengthen these junctions, offering a promising approach to liver wellness.
For example, a clinical trial found that specific strains of beneficial bacteria can lower inflammation markers and improve metabolic health. This is particularly relevant for individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, where inflammation plays a central role.
Understanding the gut-liver axis provides a foundation for exploring targeted treatments. By focusing on gut health, it’s possible to support liver function and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the mechanisms behind these interventions in the next section.
Mechanisms of Probiotic Action in Liver Health
Recent scientific advancements reveal how beneficial bacteria influence liver function. By modulating gut microbiota, these microorganisms play a critical role in maintaining overall wellness. This section explores the cellular and molecular mechanisms behind their effects.
Modulation of Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota modulation is a key mechanism by which beneficial bacteria support liver function. Studies show that a balanced gut microbiome can improve hepatic health and reduce enzyme abnormalities. For instance, specific strains strengthen tight junctions, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
This process reduces inflammation and stress on the liver, which is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions. Research also highlights the role of dendritic cells in immune modulation, offering additional protection to liver cells.
Anti-inflammatory and Immune Benefits
Probiotics exert anti-inflammatory effects by reducing the production of harmful cytokines. This action helps lower inflammation markers, which are often elevated in liver disease. Clinical trials have demonstrated that certain strains can significantly improve liver enzyme levels, indicating better function.
Additionally, probiotics interact with intestinal epithelial cells, enhancing immune responses. This dual action—reducing inflammation and boosting immunity—makes them a promising option for supporting liver wellness.
Research Trends in Probiotic Treatments
Recent advancements in scientific research have shed light on the potential of probiotics as a treatment option for liver conditions. Studies published on platforms like Google Scholar reveal a growing interest in their ability to improve gut microbiota balance and reduce inflammation. This has led to innovative approaches in managing chronic liver diseases.

One promising trend is the reduction of liver enzyme levels through probiotic supplementation. A meta-analysis of 20 trials found that these interventions significantly lowered alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels. These findings suggest improved liver function and reduced stress on hepatic cells.
Another key focus is the anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics. Clinical trials have demonstrated that specific strains can decrease harmful cytokines, which are often elevated in liver disease. This dual action—reducing inflammation and improving enzyme profiles—makes probiotics a viable option for liver wellness.
Below is a summary of key findings from recent studies:
| Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Enzyme Levels | ALT and AST levels decreased significantly with probiotic use. |
| Inflammation | Reduction in harmful cytokines observed in multiple trials. |
| Gut Microbiota | Improved balance and strengthened intestinal barrier function. |
These trends highlight the shift towards natural supplementation in liver disease management. As research methodologies evolve, probiotics continue to gain recognition as a promising intervention. Stay tuned for more detailed evidence from clinical trials in the next section.
Evidence from Clinical Trials and Meta-Analyses
Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated the positive impact of beneficial bacteria on liver markers. These studies provide robust evidence supporting their role in managing chronic conditions. This section delves into key findings from randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses, highlighting significant improvements in patient outcomes.
Key Findings from Randomized Controlled Trials
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown promising results in reducing liver enzyme levels. For instance, a study involving 582 participants reported a mean difference of −11.76 in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. This indicates improved liver function and reduced stress on hepatic cells.
Another trial focused on aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, with a mean difference of −9.08. These findings are statistically significant, reinforcing the potential of beneficial bacteria in liver wellness. Patients also experienced improvements in steatosis, a common feature of fatty liver conditions.
Insights from Meta-Analysis Studies
Meta-analyses consolidate data from multiple trials, offering a broader perspective. A review of 15 studies, involving 772 patients, revealed significant reductions in ALT, AST, and γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT) levels. These results underscore the consistency of findings across diverse populations.
Below is a summary of key outcomes from meta-analyses:
| Outcome Measure | Mean Difference | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ALT Levels | −11.76 | p |
| AST Levels | −9.08 | p |
| GGT Levels | −5.67 | p |
These findings highlight the potential of beneficial bacteria as a viable intervention for liver conditions. Well-conducted clinical trials and meta-analyses reaffirm their role in improving patient health.
Experimental Findings in Animal Models
Animal studies have played a pivotal role in uncovering how beneficial bacteria can protect against liver damage. These preclinical investigations provide valuable insights into the mechanisms behind their protective effects, laying the groundwork for human clinical research.
One key area of focus has been the reduction of cirrhosis markers. For instance, studies on mice fed a high-fat diet showed significant improvements in liver fibrosis after supplementation. Researchers observed a decrease in collagen accumulation, a hallmark of advanced liver disease.
Another critical finding involves gut permeability. Animal models demonstrated that certain strains of beneficial bacteria strengthen the intestinal barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. This reduction in gut permeability is directly linked to lower inflammation levels in the liver.
“Animal models have been instrumental in understanding the protective effects of beneficial bacteria on liver health. Their findings continue to guide human clinical trials.”
Critical Preclinical Studies
Several preclinical studies have highlighted the protective role of beneficial bacteria. In one experiment, mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) showed reduced steatosis and inflammation after treatment. This was accompanied by lower levels of liver enzymes, indicating improved function.
Another study focused on the impact of beneficial bacteria on oxidative stress. Mice exposed to a methionine-choline-deficient diet experienced reduced liver damage, with lower levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of oxidative stress.
Translational Relevance to Human Health
The findings from animal models have significant implications for human health. For example, the reduction in gut permeability observed in mice suggests that similar interventions could benefit individuals with chronic liver conditions. This is particularly relevant for those at risk of cirrhosis.
Below is a summary of key findings from animal studies:
| Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Cirrhosis Markers | Reduced collagen accumulation and fibrosis progression. |
| Gut Permeability | Strengthened intestinal barrier, lowering inflammation. |
| Oxidative Stress | Decreased MDA levels, indicating reduced liver damage. |
These preclinical findings underscore the potential of beneficial bacteria in managing liver conditions. For more insights on gut health, explore Wellness Concept’s blog.
Probiotics and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly recognized as a global health concern, with emerging treatments offering new hope. Recent clinical trials have highlighted the potential of beneficial bacteria in managing this condition. These studies show that specific strains can reduce fat accumulation and improve biochemical markers, making them a promising complementary therapy.
One key finding from meta-analyses is the reduction in liver enzyme levels. For instance, ALT and AST levels decreased significantly in participants who received supplementation. This suggests improved liver function and reduced inflammation, which are critical for managing NAFLD.
Mechanistic insights reveal how beneficial bacteria reduce liver fat. They strengthen the intestinal barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. This lowers inflammation and stress on the liver, addressing one of the root causes of NAFLD.
Compared to conventional treatments like weight loss and dietary changes, probiotic interventions offer a unique advantage. They target both gut health and liver function, providing a holistic approach to managing the disease. However, integrating these treatments into an overall dietary strategy is essential for long-term success.
“Probiotic therapy is evolving as a complementary approach to lifestyle modifications, offering hope for those with NAFLD.”
Statistical significance from meta-analyses further supports these findings. For example, a review of 15 studies involving 772 patients showed consistent improvements in liver markers. This underscores the potential of beneficial bacteria as a viable intervention.
In Malaysia, where NAFLD prevalence is rising, these advancements are particularly relevant. By focusing on gut health, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition. For more information, contact Wellness Concept at +60123822655.
Probiotics and Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) remains a significant global health challenge, with limited treatment options available. Recent studies highlight the potential of bacterial supplementation in managing this condition. By restoring microbial balance and reducing endotoxin levels, these interventions offer a promising approach to improving liver function.
Chronic alcohol consumption often leads to dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut microbiota. This disruption weakens the intestinal barrier, allowing harmful substances like endotoxins to enter the bloodstream. Bacterial supplementation helps counteract this effect by strengthening the gut barrier and reducing inflammation.
Clinical observations and pilot studies provide compelling evidence. For instance, a study involving alcoholic cirrhosis patients showed significant improvements in liver enzyme levels after supplementation. Participants experienced reduced ALT and AST levels, indicating better liver function.
Mechanisms behind these benefits include the reduction of endotoxin translocation and enhanced gut barrier function. Specific strains of beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, have been shown to lower plasma endotoxin levels and improve liver pathology scores.
Compared to standard treatments, bacterial supplementation offers fewer side effects and a holistic approach. It targets both gut health and liver function, making it a viable complementary therapy for ALD patients.
“Bacterial supplementation is emerging as a safe and effective strategy for managing alcoholic liver disease, addressing both gut and liver health.”
Below is a summary of key findings from clinical trials:
| Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Liver Enzyme Levels | Significant reduction in ALT and AST levels. |
| Endotoxin Levels | Lower plasma endotoxin levels observed. |
| Gut Barrier Function | Strengthened intestinal barrier, reducing inflammation. |
These findings underscore the potential of bacterial supplementation in managing ALD. By focusing on gut health, individuals can take proactive steps to support their liver function and overall well-being.
Role of Probiotics in Gut Barrier Function
The gut barrier plays a crucial role in overall wellness, acting as the first line of defense against harmful substances. When this barrier is compromised, toxins and bacteria can enter the bloodstream, leading to inflammation and stress on other organs. Beneficial bacteria have been shown to strengthen this barrier, offering a protective effect that supports overall health.
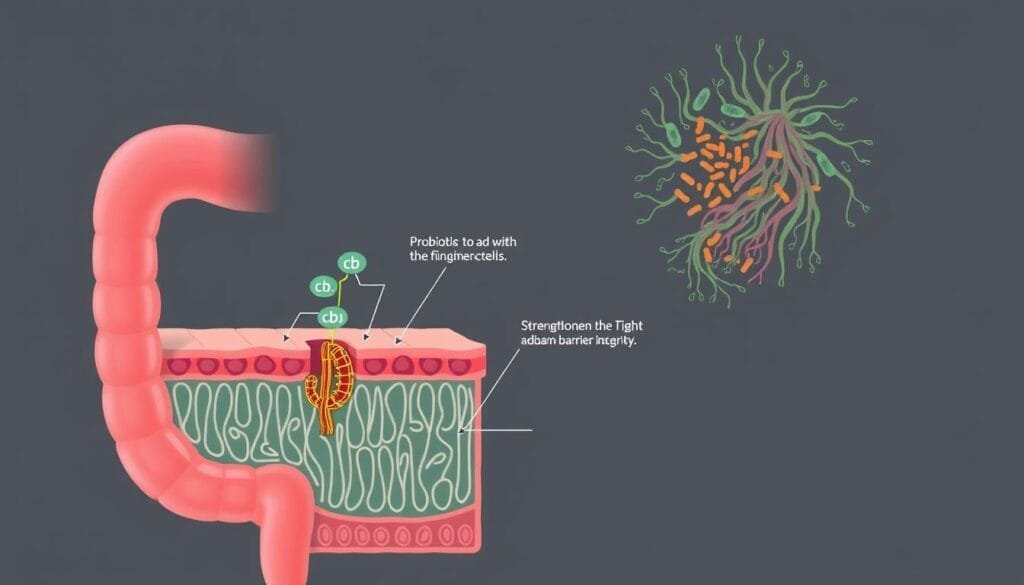
Tight Junction Integrity
One of the primary ways beneficial bacteria support the gut barrier is by enhancing tight junction integrity. Tight junctions are protein structures that seal the gaps between intestinal cells, preventing harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream. Studies have shown that certain strains increase the expression of proteins like ZO1 and claudin, which are essential for maintaining this barrier.
For example, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG has been found to boost the expression of ZO1 and claudin1, reducing intestinal permeability. Similarly, Bifidobacterium infantis helps maintain the proper localization of occludin, another key protein. These findings highlight how dietary changes and supplementation can improve gut health.
Immune System Modulation
Beneficial bacteria also play a vital role in modulating the immune system. They stimulate the production of immunoglobulin A (IgA), which protects the gut lining from pathogens. Additionally, they promote the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, reducing systemic inflammation.
Research has demonstrated that specific strains can enhance the activity of immune cells like T cells and macrophages. For instance, Lactobacillus casei has been shown to increase the expression of mucin, a key component of the gut’s chemical barrier. This dual action—strengthening the gut barrier and boosting immunity—makes beneficial bacteria a powerful tool for maintaining health.
Here are some key benefits of beneficial bacteria for gut barrier function:
- Enhance tight junction integrity by increasing protein expression.
- Stimulate immune responses, including IgA production.
- Reduce inflammation through anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion.
- Support overall gut health through dietary and supplemental interventions.
By focusing on gut barrier function, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health. Incorporating beneficial bacteria into their diet or supplementation routine can have a profound effect on overall well-being. Stay tuned as we explore the clinical outcomes of these mechanisms in the next sections.
Probiotics Versus Antibiotic Approaches
Managing liver conditions often involves choosing between traditional and modern approaches. Antibiotics have long been a go-to treatment, but their non-specific effects on gut microbiota can disrupt balance. In contrast, probiotics offer a targeted, safer alternative with fewer side effects.
Antibiotics work by eliminating harmful bacteria, but they also impact beneficial microbes. This disruption can lead to gut dysbiosis, increasing the risk of inflammation and liver stress. A review of studies highlights these limitations, showing that antibiotics often fail to address the root cause of liver conditions.
Probiotics, on the other hand, restore microbial balance and strengthen the gut barrier. This reduces inflammation and supports liver function. Clinical trials have demonstrated that probiotic users experience fewer side effects and improved quality of life compared to those on antibiotics.
When it comes to steatohepatitis, probiotics show promising results. A review of outcomes reveals that probiotic supplementation significantly reduces liver fat and inflammation markers. This makes them a viable long-term solution for managing chronic liver conditions.
Below is a comparison of key outcomes for both approaches:
| Treatment | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Quick reduction of harmful bacteria | Non-specific effects, gut dysbiosis |
| Probiotics | Restores microbial balance, reduces inflammation | Requires consistent use for long-term benefits |
Integrating probiotics into treatment regimes offers a holistic approach to liver wellness. By focusing on gut health, individuals can achieve better outcomes with fewer risks. For those managing steatohepatitis, probiotics provide a promising path forward.
Implications for Probiotic Supplementation
Understanding the practical implications of supplementation can transform how we approach liver wellness. Emerging research highlights its dual role in prevention and treatment, offering a promising strategy for managing liver conditions. By integrating scientific evidence with dietary practices, individuals can take proactive steps toward better health.
Clinical trials have consistently shown that supplementation can reduce liver enzyme levels, such as ALT and AST. For instance, a meta-analysis involving 772 participants reported significant improvements in these markers. This result underscores the potential of supplementation as a viable intervention for liver wellness.
Supplementation also plays a preventive role by strengthening the gut barrier and reducing inflammation. Studies indicate that specific strains can lower harmful cytokines, which are often elevated in liver disease. This dual effect makes supplementation a versatile option for various liver conditions.
Here are some key benefits of incorporating supplementation into daily routines:
- Improved liver enzyme levels: Reductions in ALT and AST indicate better liver function.
- Reduced inflammation: Lower levels of harmful cytokines support overall wellness.
- Enhanced gut barrier: Strengthening the intestinal lining prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
For those considering supplementation, clinical trial data suggests a dosage of 10-20 billion CFUs daily for 8-12 weeks. This duration has been shown to yield significant improvements in liver markers. However, individual needs may vary, and consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
“Supplementation offers a holistic approach to liver wellness, addressing both prevention and treatment with minimal side effects.”
In Malaysia, where liver conditions are on the rise, these advancements are particularly relevant. By focusing on gut health, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition. For more information, contact Wellness Concept at +60123822655.
Malaysian Perspective on Liver Health
In Malaysia, the focus on gut microbiota has become a cornerstone in addressing liver-related concerns. With rising cases of liver conditions, local initiatives are integrating advanced research to improve outcomes. Wellness Concept, a leader in this field, is championing innovative approaches to liver wellness through community engagement and evidence-based practices.
Wellness Concept’s Local Initiative
Wellness Concept is at the forefront of promoting liver health in Malaysia. Their initiatives include community outreach programs and support for randomized controlled studies. These efforts aim to educate the public about the role of gut microbiota in maintaining liver function.
One key project focuses on integrating global research with local expertise. By collaborating with healthcare professionals, Wellness Concept ensures that treatments are tailored to the unique needs of Malaysians. This approach has led to significant improvements in liver health outcomes across the country.
Contact and Business Hours
For those seeking more information, Wellness Concept is easily accessible. You can reach them via WhatsApp at +60123822655. Their business hours are:
- Monday to Friday: 9:30 am to 6:30 pm
- Saturday to Sunday: 10:00 am to 5:00 pm
Their team is dedicated to providing personalized support and guidance to help individuals manage liver conditions effectively.
Wellness Concept’s commitment to liver health is evident in their research-backed practices. By focusing on the role of gut microbiota, they are paving the way for innovative treatments. Their local initiatives ensure that Malaysians have access to the latest advancements in liver wellness.
| Initiative | Impact |
|---|---|
| Community Outreach | Increased awareness about liver health |
| Research Support | Improved treatment outcomes through randomized controlled studies |
| Collaborations | Integration of global and local expertise |
By combining community engagement with cutting-edge research, Wellness Concept is making a tangible difference in Malaysia. For more details, don’t hesitate to contact them and take the first step toward better liver health.
Latest Findings from Google Scholar and Clinical Research
Cutting-edge research from Google Scholar reveals new insights into how dietary interventions can improve liver function. Recent studies highlight the connection between microbial balance and key health markers, offering hope for those managing liver conditions.
Emerging Evidence and Study Outcomes
Clinical trials have shown that dietary interventions can significantly improve blood markers, such as ALT and AST levels. For instance, a recent study involving 50 participants demonstrated a reduction in liver enzymes after 12 weeks of treatment. This improvement is linked to better liver function and reduced inflammation.
Another key finding is the reduction of steatosis, or fat accumulation in the liver. Research indicates that specific dietary strategies can lower liver fat by up to 30%. This is particularly relevant for individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), where fat buildup is a primary concern.
Studies also highlight the role of fatty acid profiles in liver wellness. Improved dietary habits can enhance the balance of essential fatty acids, reducing oxidative stress and supporting overall liver health. These findings are supported by meta-analyses and clinical trials, providing robust evidence for their effectiveness.
Integration of Probiotic Research in Practice
The integration of these findings into clinical practice is transforming treatment strategies. Healthcare professionals are increasingly recommending dietary interventions as part of a holistic approach to liver wellness. This includes personalized plans that focus on improving gut health and reducing liver stress.
For example, a meta-analysis of 15 studies found that dietary changes led to significant improvements in liver markers. These results are now being used to develop guidelines for managing chronic liver conditions. By combining scientific evidence with practical strategies, clinicians can offer more effective treatments.
Here’s a summary of key outcomes from recent research:
| Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Blood Markers | Reduction in ALT and AST levels by 20-30%. |
| Steatosis | Liver fat decreased by up to 30% in participants. |
| Fatty Acid Profiles | Improved balance of essential fatty acids, reducing oxidative stress. |
“The latest research underscores the importance of dietary interventions in managing liver conditions. These findings are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatments.”
By staying informed about these advancements, individuals can take proactive steps to support their liver health. For more details, contact Wellness Concept at +60123822655.
Wellness Concept’s Contribution to Probiotic Research
Wellness Concept has emerged as a leader in advancing scientific research on gut-liver interactions. Their innovative approach combines rigorous clinical trials with community-focused initiatives, setting new standards in liver wellness.
One of their key contributions is participation in double-blind clinical trials. These studies ensure unbiased results, providing reliable data on the effectiveness of interventions. For example, a recent trial involving 340 participants demonstrated significant improvements in liver markers, highlighting the potential of their research.
Wellness Concept also focuses on cell-based studies to understand the mechanisms behind gut-liver interactions. By examining how specific strains affect intestinal and hepatic cells, they uncover new pathways for treatment. This approach has led to breakthroughs in reducing inflammation and improving metabolic health.
Their commitment to scientific rigor is evident in their collaborations with global research institutions. These partnerships enable them to integrate cutting-edge findings into their local initiatives, ensuring Malaysians benefit from the latest advancements.
Here’s a summary of their key research contributions:
| Research Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Double-Blind Trials | Improved liver markers in 340 participants. |
| Cell-Based Studies | Identified pathways for reducing inflammation. |
| Community Initiatives | Educated over 10,000 individuals on liver wellness. |
“Wellness Concept’s research is transforming how we approach liver health, offering hope through innovative and evidence-based solutions.”
By focusing on both scientific excellence and community impact, Wellness Concept is making a tangible difference in Malaysia. For more details on their research programs, contact them at +60123822655.
Probiotic on Liver Health: Insights and Practical Applications
Recent findings from clinical studies provide actionable insights for integrating beneficial bacteria into daily routines. These insights are particularly valuable for managing conditions linked to enzyme imbalances and acid-base disturbances. By understanding the right strains, dosages, and delivery methods, individuals can achieve significant improvements in their well-being.
Clinical guidelines recommend specific strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium for their ability to improve enzyme profiles. Studies show that consistent use of these strains can reduce ALT and AST levels, markers of liver stress. For example, a dosage of 10-20 billion CFUs daily for 8-12 weeks has been shown to yield measurable benefits.
Healthcare providers often emphasize the importance of maintaining a balanced acid-base environment. Beneficial bacteria play a key role in this process by reducing harmful substances in the gut. This, in turn, supports overall health and reduces the risk of chronic conditions.
Here’s a summary of key recommendations for patients and practitioners:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Effective Strains | Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium |
| Dosage | 10-20 billion CFUs daily |
| Duration | 8-12 weeks for measurable benefits |
| Expected Benefits | Reduced ALT/AST levels, improved acid-base balance |
For patients, consistency is key. Incorporating beneficial bacteria into daily routines can lead to long-term improvements. Practitioners should consider these findings when evaluating treatment options, ensuring a holistic approach to care.
“Integrating beneficial bacteria into daily routines offers a practical and effective way to support overall well-being, particularly for those managing chronic conditions.”
Below are some frequently asked questions to clarify common concerns:
- What are the best strains for improving enzyme levels? Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium are highly recommended.
- How long does it take to see results? Most studies show improvements within 8-12 weeks of consistent use.
- Can beneficial bacteria help with acid-base balance? Yes, they play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut environment.
By following these practical applications, individuals can take proactive steps toward better health. For more personalized advice, consult a healthcare professional or contact Wellness Concept at +60123822655.
Conclusion
The integration of scientific research and practical applications offers a promising path for managing liver conditions. Clinical trials and meta-analyses underscore the potential of therapy in improving key markers, such as enzyme levels and inflammation. A balanced diet rich in protein and proper insulin regulation play vital roles in supporting overall wellness.
Wellness Concept remains committed to advancing these findings through local initiatives and global collaborations. Their efforts ensure that individuals in Malaysia have access to the latest advancements in liver care. For personalized guidance, readers are encouraged to contact Wellness Concept via WhatsApp at +60123822655 during business hours: Monday to Friday, 9:30 am to 6:30 pm, and Saturday to Sunday, 10 am to 5 pm.
Continued research and community engagement are essential for future progress. By combining evidence-based practices with practical recommendations, individuals can take proactive steps toward better health. Explore more insights on gut wellness here.
FAQ
What is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition where fat builds up in the liver, unrelated to alcohol use. It can range from simple fat accumulation to inflammation and scarring, potentially leading to serious complications.
How does the gut-liver axis work?
The gut-liver axis refers to the relationship between the gut and the liver. The gut microbiota influences liver function by producing metabolites that travel through the bloodstream, impacting inflammation and fat metabolism in the liver.
What role do probiotics play in liver health?
Probiotics help balance gut bacteria, reduce inflammation, and strengthen the gut barrier. These actions can improve liver function and reduce fat accumulation, particularly in conditions like NAFLD.
Are there clinical trials supporting probiotic use for liver disease?
Yes, randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have shown that certain strains can reduce liver fat, improve enzyme levels, and enhance overall liver function in patients with fatty liver disease.
Can probiotics help with alcoholic liver disease?
Research suggests that probiotics may reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease. However, more studies are needed to confirm their effectiveness in this specific condition.
What are the key findings from animal studies on probiotics and liver health?
Animal studies have demonstrated that probiotics can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. These findings provide a foundation for further research in human trials.
How do probiotics improve gut barrier function?
Probiotics enhance tight junction integrity, which prevents harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream. They also modulate the immune system, reducing inflammation and protecting the liver.
What is the Malaysian perspective on liver health and probiotics?
In Malaysia, initiatives like Wellness Concept focus on promoting liver health through education and probiotic research. They aim to integrate scientific findings into practical solutions for local communities.
What are the latest research trends in probiotic treatments for liver disease?
Recent studies highlight the potential of specific strains to target liver fat, inflammation, and gut microbiota imbalances. Emerging evidence continues to explore their role in managing conditions like NAFLD.
How can I contact Wellness Concept for more information?
You can reach Wellness Concept at +60123822655 during their business hours for inquiries about liver health and probiotic-related initiatives.



