Currently Empty: RM0.00
One in five people with chronic skin inflammation report changes after adjusting gut support, a surprising signal that the gut-skin link may matter more than most expect.
Wellness Concept explains how live microbes can balance the microbiome, stimulate T cells, and reduce inflammation that shows up on the skin. Early research shows these microbes may help some with psoriasis and may ease atopic dermatitis symptoms in adults, while traditional care still uses topical agents, systemic drugs, biologics, and light therapies.
The guide presents a clear, friendly way to learn what evidence exists today, where it remains limited, and how these approaches fit alongside doctor‑recommended treatments. Readers in Malaysia can reach Wellness Concept via WhatsApp at +60123822655 during business hours: Monday–Friday 9:30 am–6:30 pm; Saturday 10 am–5 pm; Sunday Closed.
Key Takeaways
- Beneficial microbes may help balance gut and skin inflammation, but results vary.
- They should complement, not replace, established medical treatments.
- Research is growing; some strains show promising reductions in inflammatory markers.
- Everyday fermented foods and targeted approaches can be practical starting points.
- Consistency and medical oversight improve chances of a positive outcome.
Understanding the role of probiotics in skin conditions today
Researchers have tracked links between gut microbes and skin inflammation since the 1990s. This long view shows both promise and mixed outcomes in clinical work.
What they are: Live cultures of helpful bacteria that may change the gut environment. When these organisms shift the microbiome toward balance, the immune system can respond less aggressively to triggers that show on the skin.
Studies suggest that expanding helpful gut bacteria can modulate T cells and lower systemic inflammation. Results vary because every person has a unique microbial mix and immune setpoint.
For plaque conditions like psoriasis, research since the 1990s points to a growing gut‑skin link. Evidence for atopic dermatitis remains mixed: some recent meta‑analyses report symptom drops with certain Lactobacillus strains, while earlier reviews saw little benefit.
- Realistic benefits: Possible symptom relief for some people, not a universal cure.
- Practical note: Effects depend on strain, dose, and time.
Wellness Concept can help interpret studies and suggest safe next steps. Message +60123822655 on WhatsApp during business hours to learn more.
How the gut-skin-immune axis works
The gut, immune signals, and skin form a linked system that shapes visible health. This section explains how microbes in the digestive tract can change immune responses and lead to skin inflammation.
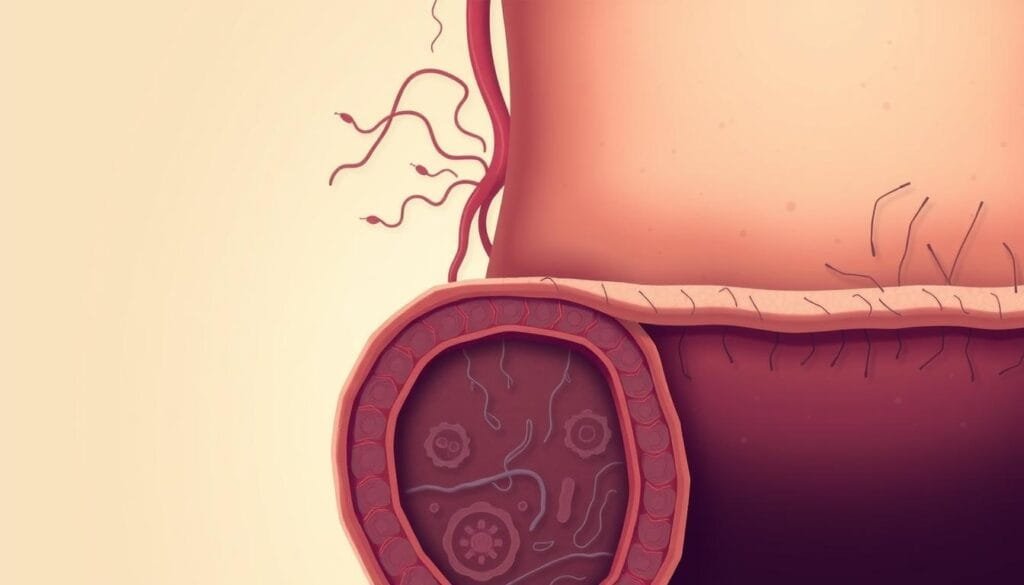
Gut microbiota balance, T cells, and systemic inflammation
Balanced gut microbiota helps T cells act calmly. When helpful bacteria thrive, immune responses tend to be steadier and systemic inflammation drops.
This can reduce flares that show up on the skin.
Intestinal permeability and its link to skin inflammation
When the intestines lose barrier strength, particles may enter circulation and trigger immune activation.
A 2018 study linked a weakened intestinal barrier, microbiome imbalance, and immune dysfunction in plaque psoriasis.
These pathways help explain why gut-targeted steps might ease skin inflammation.
Beneficial bacteria versus pathogenic bacteria on skin and in the gut
Some species protect the body; others drive inflammation. Excess inflammation-causing bacteria in the gut often appears in people with psoriasis.
Pathogens such as streptococcus can trigger guttate flares, while shifts in skin genera like Corynebacterium, Propionibacterium, and Staphylococcus relate to chronic plaques.
“Shifting bacterial profiles can change immune activity and downstream effects on skin comfort.”
Wellness Concept can guide next steps. Contact Wellness Concept on WhatsApp +60123822655 during business hours for personalised advice.
Evidence on probiotics for psoriasis: what studies suggest
Small clinical trials and case reports now explore whether certain live strains can shift immune markers tied to chronic skin plaques.
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains and inflammatory biomarkers
Notable data include a 2013 study where Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 lowered inflammatory biomarkers after eight weeks. A 2012 case report described a woman with pustular psoriasis who showed visible improvement within two weeks on a Lactobacillus product.
Research highlights and limitations
These reports show promise but remain small. Researchers often use different strains, doses, and outcome measures. That variation makes broad conclusions difficult.
- What this means: Some people see reduced inflammation and clearer skin within weeks.
- Limits: Small sample sizes and mixed protocols weaken certainty.
- Care advice: Use supplements as an adjunct to standard treatments such as topicals, phototherapy, or systemic therapies. The FDA has not approved these products to treat disease.
Wellness Concept can help select options and track results. Message +60123822655 on WhatsApp during business hours to ask about choices and keeping a flare log.
Evidence on probiotics for eczema: potential benefits and open questions
Clinical summaries suggest some live cultures reduce immune-driven rash in adults, but results differ by strain and study design. This growing body of work aims to link targeted bacterial support to calmer immune responses in atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis, immune dysregulation, and beneficial bacteria
Atopic dermatitis reflects immune imbalance that shows up as itchy, inflamed skin. Researchers study how certain gut bacteria can shift immune signaling and ease symptoms.
Children with this condition often show fewer helpful gut bacteria and more harmful species. That pattern suggests microbiome support could be useful while clinicians evaluate treatment plans.
What recent reviews and meta-analyses say about strains and dosage
A 2023 meta-analysis of nine trials reported that specific Lactobacillus strains—L. salivarius, L. acidophilus, and L. plantarum—were linked to meaningful symptom drops in adults with moderate to severe disease.
However, a 2018 review found little or no difference on self-reported outcomes. Key limits include small sample sizes, varied doses, and mixed follow‑up lengths.
“Certain strains show promise, but optimal dose and duration remain unclear.”
| Study Type | Noted Strains | Main Finding |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 meta-analysis (9 studies) | L. salivarius, L. acidophilus, L. plantarum | Significant symptom reduction in adults; dose unclear |
| 2018 systematic review | Mixed strains across trials | No clear benefit on self-reported measures |
| Paediatric microbiome surveys | Lower beneficial bacteria in children | Supports role for targeted microbiome strategies |
- Takeaway: Some adults may see benefits, but outcomes vary by strain, dose, and study quality.
- Live cultures should complement, not replace, clinician‑recommended care.
- Discuss specific strains and measurable symptom goals with a provider and track changes over weeks.
Readers in Malaysia can contact Wellness Concept on WhatsApp at +60123822655 during business hours for friendly guidance on choices and monitoring.
Probiotics for eczema and psoriasis: practical ways to get started
A practical plan helps people test which live-culture foods and products suit their body. Start small and stay consistent. Small steps make it easier to spot real changes in skin and gut health.
Food sources of live beneficial bacteria
Everyday foods can add helpful microbes without major changes. Try yogurt, acidophilus milk, sourdough bread, pickles, and fermented cheeses such as Gouda, cheddar, Swiss, or parmesan.
Supplements, strains to know, and safety
When choosing probiotic supplements, look for studied strains like Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 and certain Lactobacillus types. Read labels for strain ID and colony-forming units (CFUs).
Safety tips: Start low and go slow. Discuss any supplement or supplement changes with medical professionals, especially when on medications or managing chronic conditions.
Tracking symptoms and working with treatments
Keep a simple log of products, doses, meal timing, and symptoms such as itch, redness, or flare frequency. Note what was eaten and any skin changes over weeks.
- Pair new foods with meals and set reminders to keep habits steady.
- Coordinate new products with dermatology treatments and prescriptions.
- Check dairy sensitivity before adding fermented dairy items.
“Small, steady steps help find what supports healthy skin while staying aligned with clinical care.”
If readers want product guidance or help fitting new steps into a care plan, message Wellness Concept on WhatsApp at +60123822655. Hours: Monday–Friday 9:30 am–6:30 pm; Saturday 10 am–5 pm; Sunday Closed.
Wellness Concept in Malaysia: guidance, products, and support
Wellness Concept in Malaysia offers friendly, evidence‑informed help to people who want to add microbiome steps into everyday skin care. The team works with clinical context and personal goals so changes fit ongoing care plans.

Talk to Wellness Concept on WhatsApp: +60123822655
Clients may message the team to review product options, discuss probiotic supplements, and plan safe steps that align with medical treatments. Staffed professionals explain likely benefits and how to track progress.
Business hours
Monday: 9:30 am–6:30 pm
Tuesday: 9:30 am–6:30 pm
Wednesday: 9:30 am–6:30 pm
Thursday: 9:30 am–6:30 pm
Friday: 9:30 am–6:30 pm
Saturday: 10:00 am–5:00 pm
Sunday: Closed
- Personalised reviews: professionals help match options to skin type, psoriasis history, or eczema concerns.
- Safety first: suggestions respect medications, allergies, and overall health.
- Practical plans: simple ways to include fermented foods or supplements with tracking tips.
| Service | What they do | Best time to contact |
|---|---|---|
| Product review | Assess strains, CFUs, and label clarity | Weekdays during business hours |
| Care planning | Create stepwise plans that align with dermatology treatments | Any weekday; Saturday by appointment |
| Progress tracking | Help set symptom logs and milestones | Ongoing support via WhatsApp |
“Small, consistent steps guided by professionals make it easier to spot real benefits while keeping medical safety central.”
Conclusion
This closing note sums up what current studies show, what remains uncertain, and how practical steps can fit into usual care.
Key takeaways: Select strains such as Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 and some Lactobacillus species have shown promise in lowering inflammatory markers. Results vary, so these options should complement established treatments rather than replace them.
Practical steps include adding fermented foods, trying a targeted supplement with clinician input, and keeping a simple symptom log to watch effects over weeks. Working with professionals helps protect safety and supports steady progress.
For friendly assistance in Malaysia, contact Wellness Concept on WhatsApp +60123822655 during business hours: Monday–Friday 9:30 am–6:30 pm; Saturday 10:00 am–5:00 pm; Sunday Closed.
FAQ
What role does the gut-skin-immune axis play in skin inflammation?
The gut-skin-immune axis links intestinal bacteria, immune cells, and skin health. When gut microbiota stay balanced, they help regulate T cells and inflammatory signals. If the intestines become more permeable or the bacterial mix shifts toward harmful species, immune activation can increase and worsen skin inflammation. Maintaining a healthy microbiome supports lower systemic inflammation and healthier skin.
Which bacterial strains have the most evidence for improving skin-related inflammation?
Studies have focused on Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, which can reduce inflammatory biomarkers in some trials. Specific strains such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum appear most often in research, but results vary by strain, dose, and the population studied. Clinicians recommend strain-specific evidence when selecting a supplement or fermented food.
Can taking supplements replace prescribed treatments for chronic skin conditions?
No. Supplements and fermented foods can be a complementary approach but should not replace dermatologist-prescribed therapies. People should discuss any new supplement or diet change with their medical provider to ensure it fits their treatment plan and won’t interfere with medications.
How soon might someone notice changes in their skin after adjusting gut health?
Responses vary. Some people report improvement within weeks, while others need months. Clinical trials often run 8–12 weeks before measurable changes appear. Tracking symptoms, photos, and flare frequency helps both patients and clinicians assess progress.
Are there risks or side effects to using live bacterial supplements or fermented foods?
Most healthy adults tolerate live bacterial foods and supplements well. Mild digestive symptoms can occur initially. People with weakened immune systems, severe illness, or those on certain medications should consult a clinician first, as rare infections have been reported in vulnerable groups.
What foods provide live beneficial bacteria that might support skin health?
Common sources include yogurt with live cultures, kefir, tempeh, miso, sauerkraut, kombucha, and certain pickles. Choosing unpasteurized or raw-fermented products preserves live bacteria. Including a variety of fiber-rich foods helps feed beneficial gut microbes.
How should someone choose a supplement to support skin and gut health?
Look for products that list specific strains, colony-forming units (CFUs) at the time of manufacture, and third-party testing or good manufacturing practices. Prefer formulas studied for skin or immune outcomes. Discuss brand choices with a pharmacist or clinician, especially if taking other medications.
What do recent reviews and meta-analyses say about benefits for atopic dermatitis?
Reviews show modest benefits in some groups, particularly in children, with certain strains and higher doses. However, heterogeneity in study design, strains used, and outcome measures means conclusions remain cautious. More standardized, high-quality trials are needed to confirm long-term effects and optimal regimens.
How does intestinal permeability relate to flare-ups of chronic skin conditions?
Increased intestinal permeability, sometimes called “leaky gut,” may allow bacterial components and metabolites into circulation, triggering systemic immune responses. That immune activation can worsen skin inflammation in susceptible people. Addressing diet, gut microbes, and gut lining health can help reduce this effect.
Are there local resources in Malaysia for guidance and products related to gut-skin wellness?
Wellness Concept in Malaysia offers guidance and products tailored to gut and skin support. People can contact them via WhatsApp at +60123822655 during business hours: Mon–Fri 9:30 am–6:30 pm and Sat 10 am–5 pm. Consulting local healthcare professionals ensures recommendations match individual medical needs.



